Product features and application fields of aramid IIIA flame-retardant fabrics
Product features of aramid IIIA flame-retardant fabrics
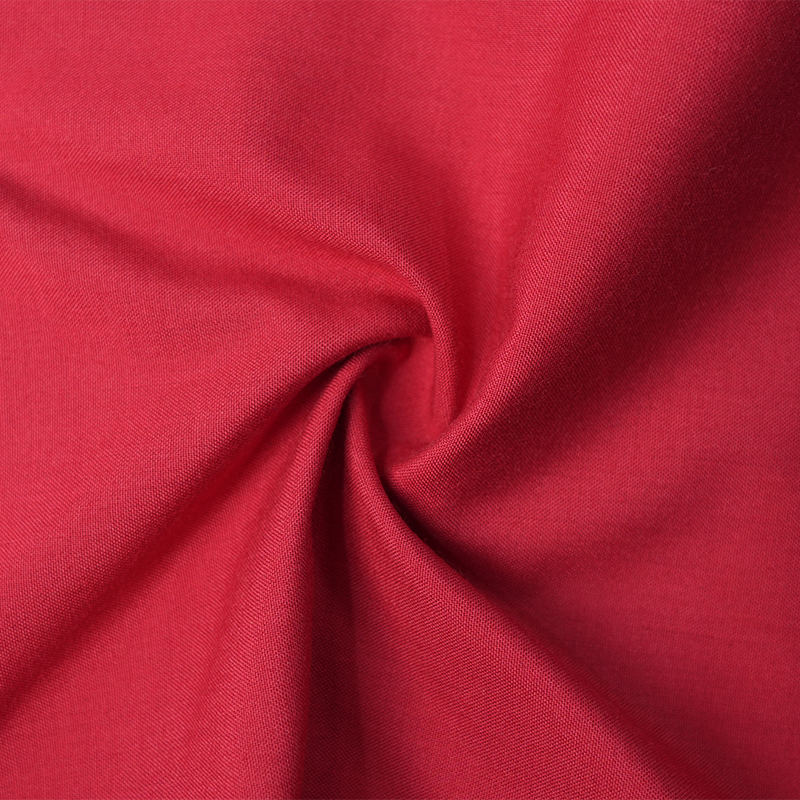
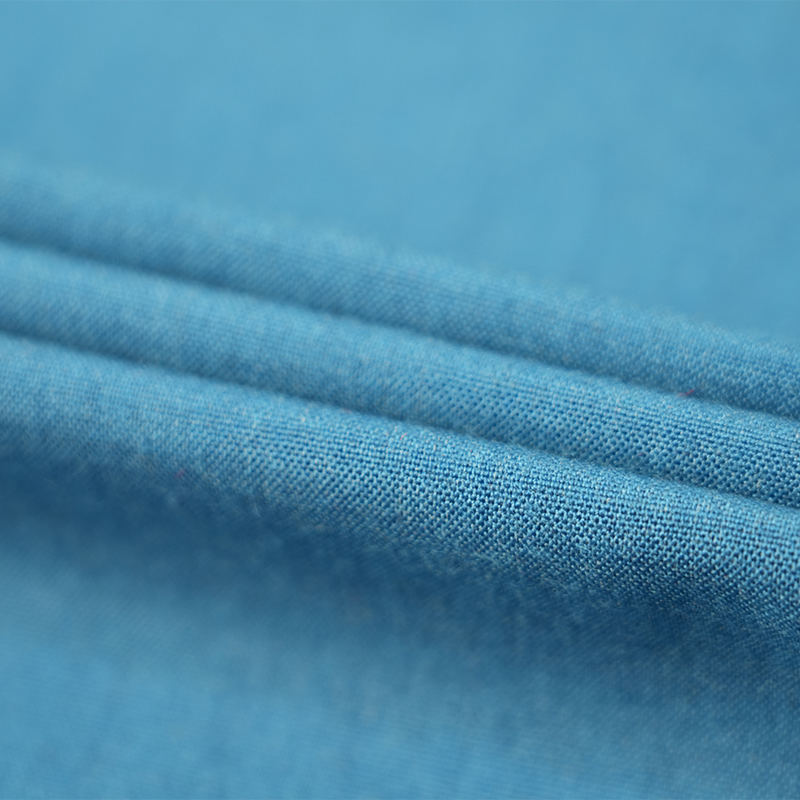
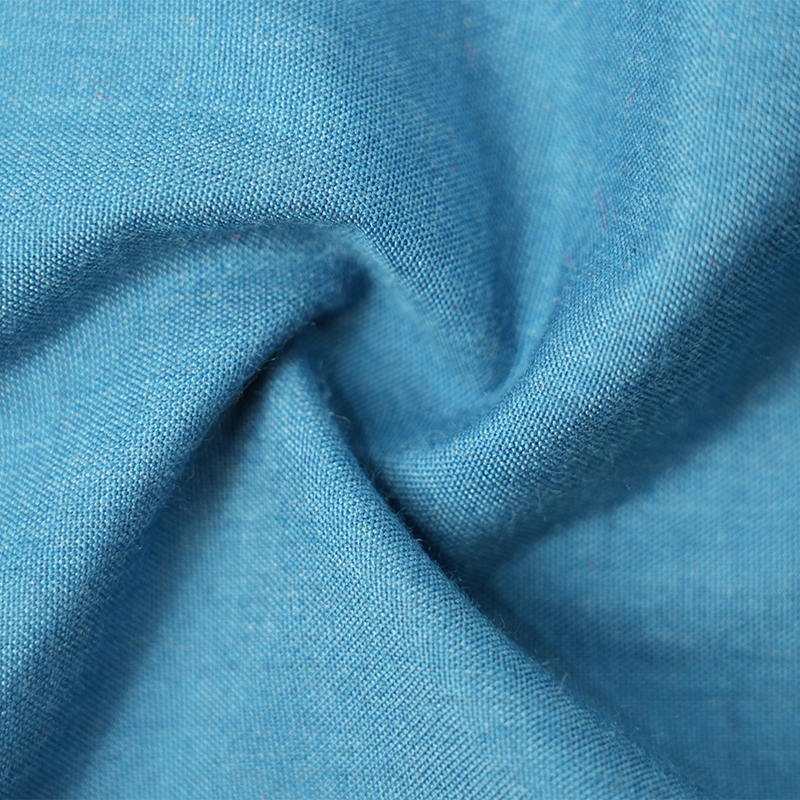
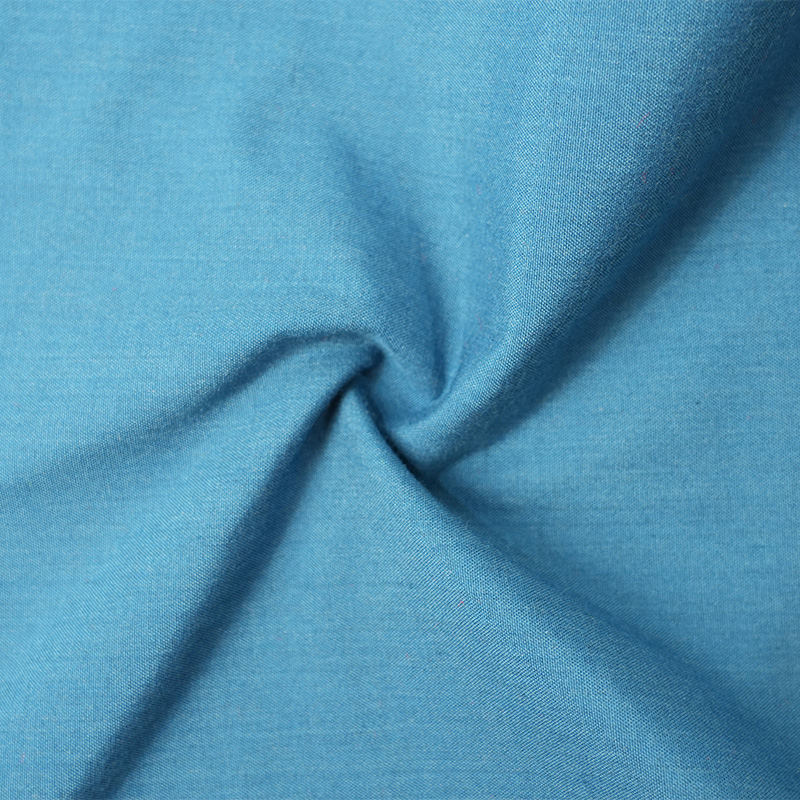
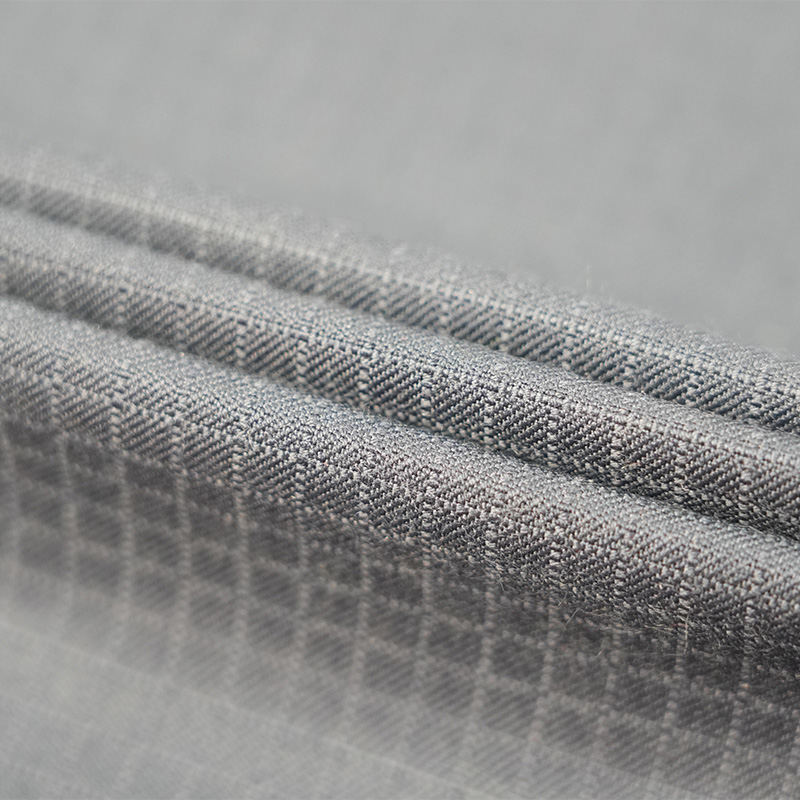
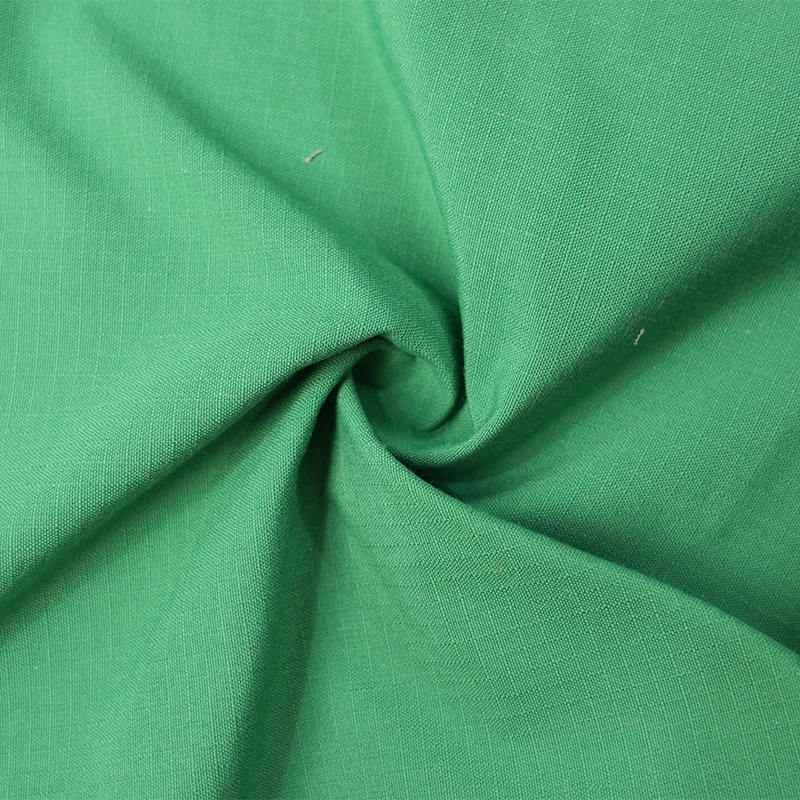
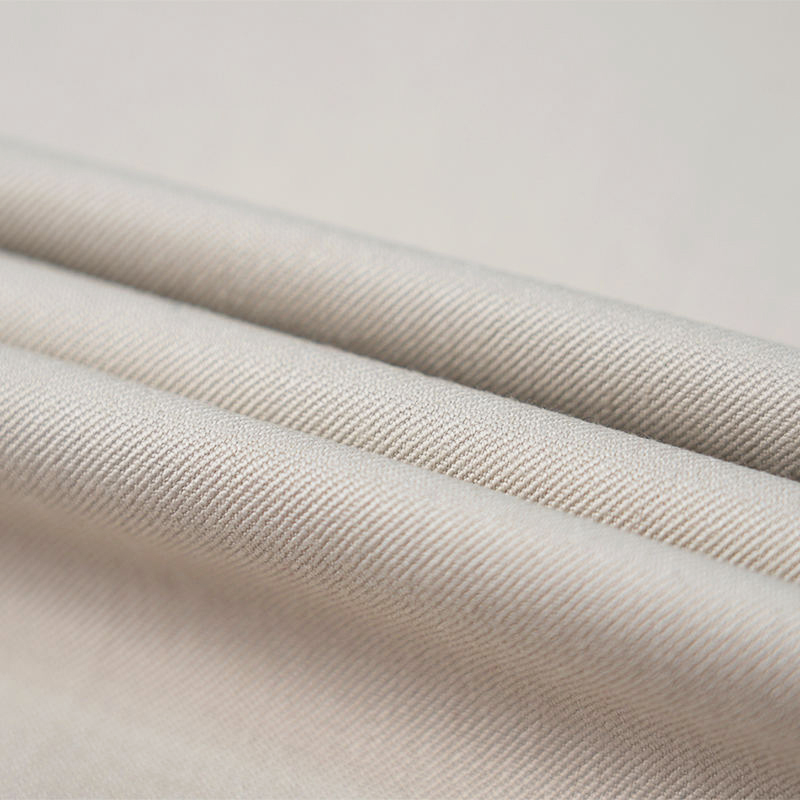
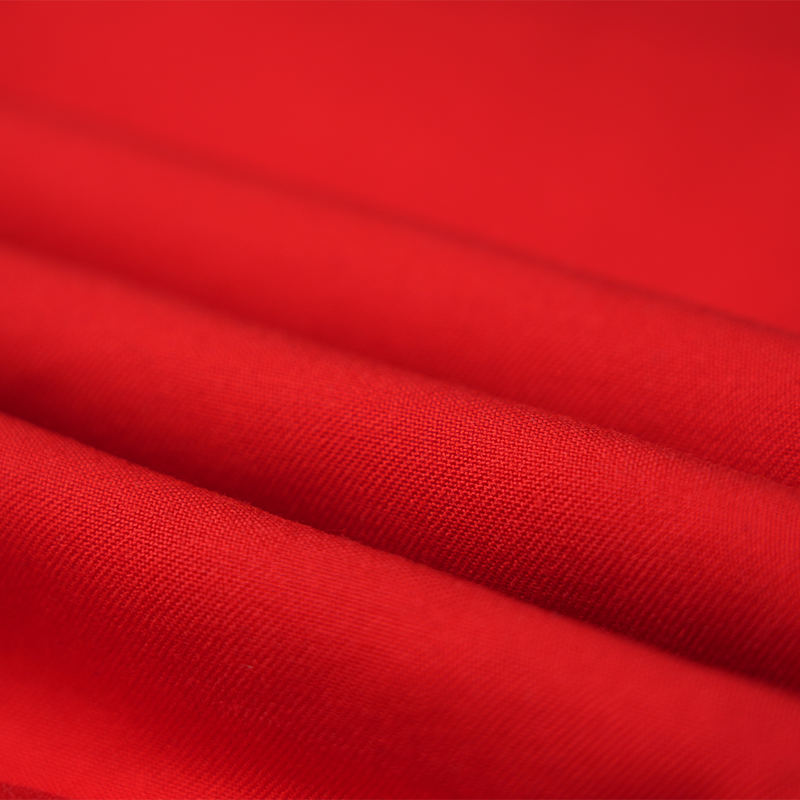
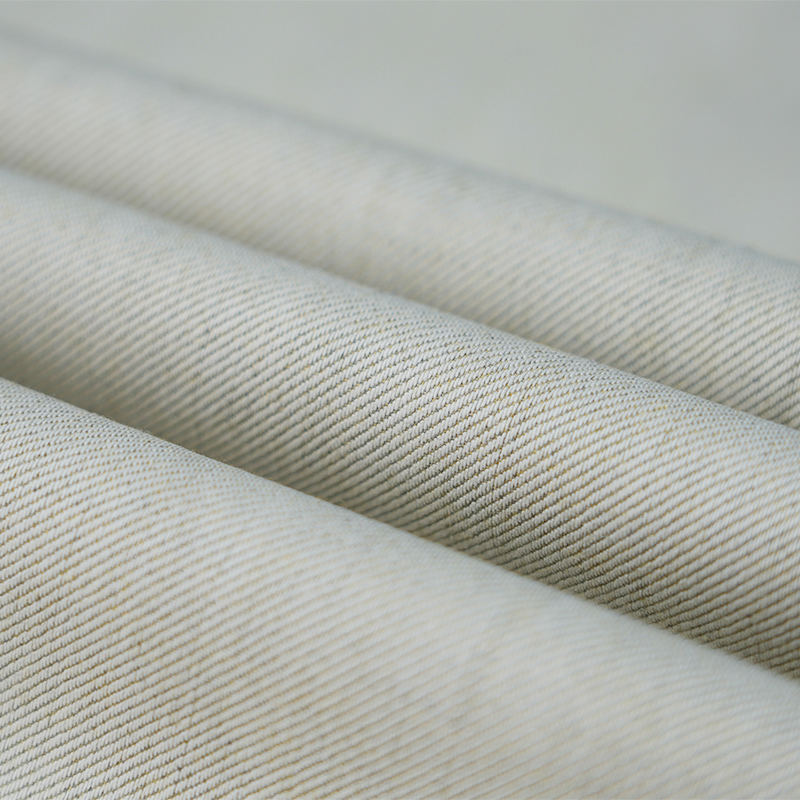
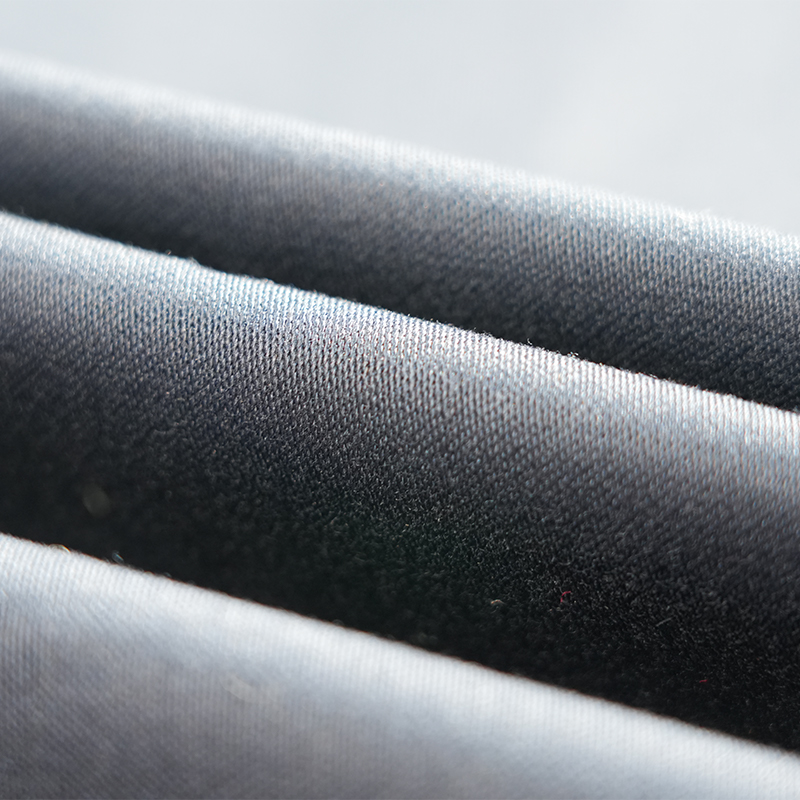
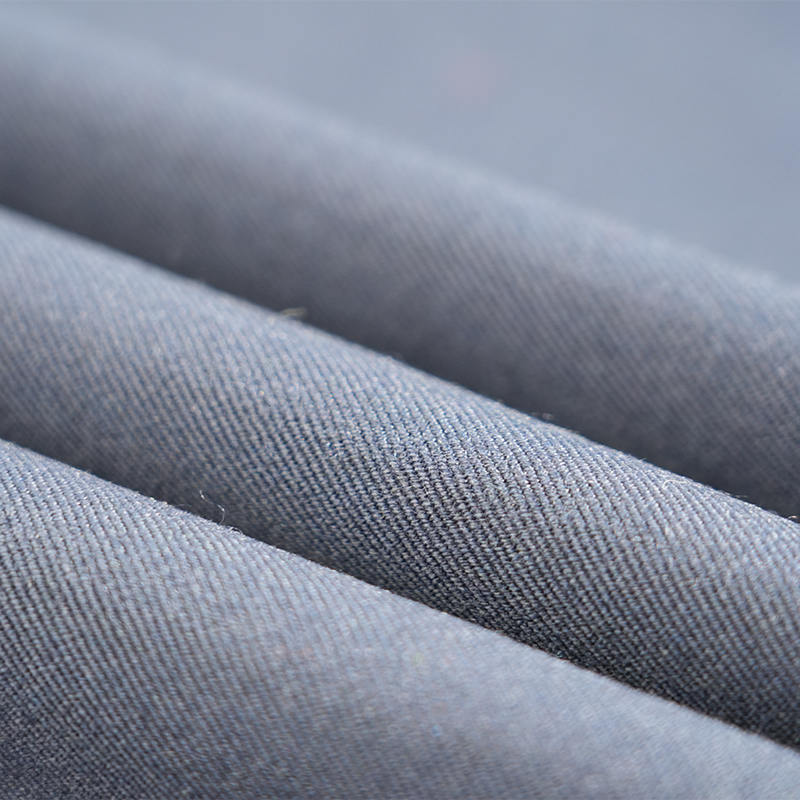
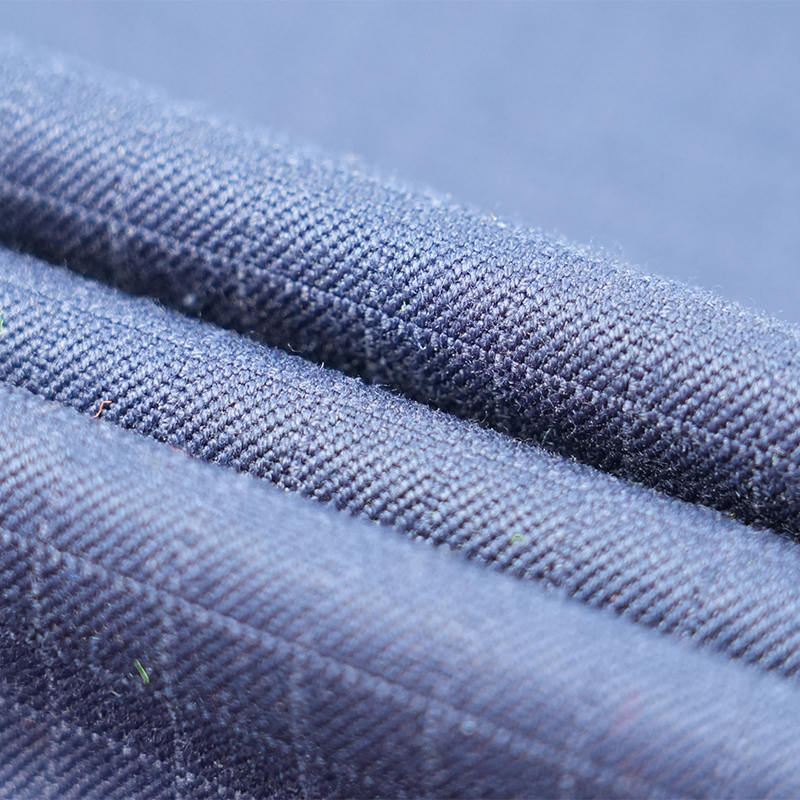
Aramid IIIA flame-retardant fabrics are made of high-performance aramid fibers, which have excellent flame retardancy, high temperature resistance and mechanical strength. Its limiting oxygen index (LOI) is ≥28%. It does not spontaneously ignite or melt when exposed to fire, and can quickly form a dense carbonized layer to effectively isolate high temperature and flames. The fabric has excellent tear resistance, abrasion resistance and antistatic properties, while remaining soft and breathable, and comfortable to wear. In addition, aramid IIIA fiber has excellent chemical corrosion resistance and UV resistance, is suitable for long-term operation in harsh environments, complies with international safety standards such as EN ISO 11612 and NFPA 2112, and is an ideal material for high-end protective equipment.
Application scope of aramid IIIA flame-retardant fabrics
Aramid IIIA flame-retardant fabrics are widely used in high-risk industries such as petrochemicals, electric power metallurgy, fire emergency, aerospace, etc., and are suitable for the production of flame-retardant protective clothing, welding work clothes, fire fighting clothing and other personal protective equipment. In scenes such as steelmaking, welding, and arc operations, it can effectively protect against high-temperature sparks and molten metal splashes; in the petrochemical and power industries, it can be used to make high-temperature resistant insulating materials or equipment protective covers. In addition, the fabric is also suitable for special fields such as military and racing, providing reliable thermal protection and safety guarantees for practitioners.
Working principle of aramid IIIA flame-retardant fabric
The protection mechanism of aramid IIIA flame-retardant fabric is based on the intrinsic flame-retardant properties of the fiber and the high-temperature carbonization barrier effect. Its aramid fiber molecular structure contains a large number of aromatic rings and amide bonds. When it encounters fire, it decomposes and absorbs heat, reduces the combustion temperature, and forms a stable carbonization layer to isolate oxygen and heat transfer. The fiber can still maintain a high strength above 400°C, can withstand high temperatures of 800°C~1000°C for a short time, and will not produce droplets or release toxic gases. In addition, some products undergo special finishing processes (such as flame-retardant coatings or composite treatments) to further enhance their fire resistance and durability, ensuring that they can still provide lasting protection under extreme conditions.

 EN
EN 中文简体
中文简体 English
English русский
русский Español
Español Português
Português عربى
عربى